Randomly Lost Randomly Found Again in the Gaps of the Years
What is RAM?
RAM (Random Access Memory) is the hardware in a computing device where the operating system (Bone), application programs and data in electric current apply are kept so they tin be quickly reached by the device'south processor. RAM is the master memory in a estimator. It is much faster to read from and write to than other kinds of storage, such as a hard deejay drive (HDD), solid-land bulldoze (SSD) or optical bulldoze.
Random Admission Memory is volatile. That means data is retained in RAM equally long every bit the reckoner is on, simply it is lost when the computer is turned off. When the computer is rebooted, the Bone and other files are reloaded into RAM, usually from an HDD or SSD.
Function of RAM
Because of its volatility, RAM can't store permanent information. RAM tin can be compared to a person'southward short-term memory, and a hard disk drive to a person's long-term memory. Brusque-term retentiveness is focused on immediate piece of work, but information technology tin only go along a express number of facts in view at any ane time. When a person's short-term retentivity fills up, it can be refreshed with facts stored in the brain's long-term retentivity.
A computer also works this fashion. If RAM fills up, the reckoner's processor must repeatedly get to the hard disk to overlay the old data in RAM with new information. This process slows the computer's functioning.

A estimator's hard disk can become completely full of information and unable to take whatsoever more, just RAM won't run out of memory. Nevertheless, the combination of RAM and storage memory can be completely used upwards.
How does RAM piece of work?
The termrandom access as applied to RAM comes from the fact that any storage location, also known as whatever memory address, tin can be accessed directly. Originally, the termRandom Access Memory was used to distinguish regular core memory from offline memory.
Offline retentivity typically referred to magnetic tape from which a specific piece of data could only be accessed by locating the address sequentially, starting at the outset of the record. RAM is organized and controlled in a way that enables data to be stored and retrieved directly to and from specific locations.
Other types of storage -- such every bit the difficult bulldoze and CD-ROM-- are also accessed direct or randomly, merely the termrandom access isn't used to describe these other types of storage.
RAM is similar in concept to a set of boxes in which each box tin hold a 0 or a 1. Each box has a unique accost that is found by counting across the columns and down the rows. A ready of RAM boxes is called an assortment, and each box is known as a cell.
To find a specific cell, the RAM controller sends the column and row accost down a sparse electrical line etched into the chip. Each row and cavalcade in a RAM array has its ain address line. Any data that'south read flows back on a separate information line.
RAM is physically pocket-sized and stored in microchips. Information technology's also small in terms of the corporeality of information information technology can agree. A typical laptop computer may come with 8 gigabytes of RAM, while a hd can concord 10 terabytes.
A hard drive, on the other manus, stores data on the magnetized surface of what looks like a vinyl record. Alternatively, an SSD stores data in memory chips that, unlike RAM, are nonvolatile. They don't depend on having constant power and won't lose data once the power is turned off. RAM microchips are gathered together into retentiveness modules. These plug into slots in a computer'south motherboard. A bus, or a set up of electrical paths, is used to connect the motherboard slots to the processor.
Most PCs enable users to add together RAM modules upward to a certain limit. Having more RAM in a computer cuts down on the number of times the processor must read information from the hard disk, an operation that takes longer than reading data from RAM. RAM access time is in nanoseconds, while storage retentivity access time is in milliseconds.
How much RAM do y'all need?
The amount of RAM needed all depends on what the user is doing. When video editing, for example, information technology'south recommended that a organization have at least 16 GB RAM, though more is desirable. For photograph editing using Photoshop, Adobe recommends a system take at least 3GB of RAM to run Photoshop CC on a Mac. All the same, if the user is working with other applications at the aforementioned time, fifty-fifty 8GB of RAM tin can slow things down.
Types of RAM
RAM comes in two primary forms:
- Dynamic Random Admission Memory ( DRAM ) makes up the typical computing device'south RAM, and as was previously noted, it needs that ability to be on to retain stored data.
Each DRAM cell has a charge or lack of charge held in an electrical capacitor. This data must exist constantly refreshed with an electronic charge every few milliseconds to compensate for leaks from the capacitator. A transistor serves as a gate, determining whether a capacitor'southward value can be read or written.
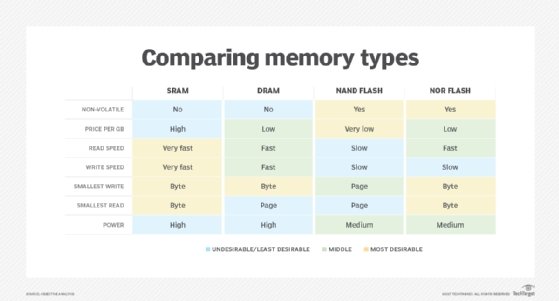
- Static Random Access Memory ( SRAM ) also needs constant power to hold on to data, but it doesn't need to be continually refreshed the way DRAM does.
In SRAM, instead of a capacitor holding the charge, the transistor acts equally a switch, with one position serving as 1 and the other position as 0. Static RAM requires several transistors to retain one bit of information compared to dynamic RAM which needs only one transistor per bit. Every bit a result, SRAM chips are much larger and more expensive than an equivalent amount of DRAM.
However, SRAM is significantly faster and uses less ability than DRAM. The price and speed differences mean static RAM is mainly used in pocket-size amounts as cache retentivity inside a computer's processor.
History of RAM: RAM vs. SDRAM
RAM was originally asynchronous because the RAM microchips had a unlike clock speed than the computer's processor. This was a problem every bit processors became more powerful and RAM couldn't keep up with the processor's requests for information.
In the early 1990s, clock speeds were synchronized with the introduction of synchronous dynamic RAM, or SDRAM. By synchronizing a reckoner'southward memory with the inputs from the processor, computers were able to execute tasks faster.
However, the original single data rate SDRAM (SDR SDRAM) reached its limit speedily. Effectually the yr 2000, double information charge per unit synchronous Random Access Retentiveness (DDR SRAM) was developed. This moved data twice in a single clock cycle, at the start and the stop.
DDR SDRAM has evolved three times, with DDR2, DDR3 and DDR4, and each iteration has brought improved information throughput speeds and reduced ability use. However, each DDR version has been incompatible with before ones because, with each iteration, data is handled in larger batches.

GDDR SDRAM
Graphics double information rate (GDDR) SDRAM is used in graphics and video cards. Like DDR SDRAM, the technology enables data to be moved at various points in a CPU clock cycle. Withal, it runs at higher voltages and has less strict timing than DDR SDRAM.
With parallel tasks, such as 2D and 3D video rendering, tight access times aren't as necessary, and GDDR can enable the higher speeds and memory bandwidth needed for GPU functioning.
Similar to DDR, GDDR has gone through several generations of development, with each providing more performance and lower ability consumption. GDDR6 is the latest generation of graphics memory.
RAM vs. virtual memory
A calculator can run brusque on retentivity, especially when running multiple programs simultaneously. Operating systems tin can compensate for concrete memory shortfalls by creating virtual memory.
With virtual retention, information is temporarily transferred from RAM to disk storage, and virtual accost space is increased using agile memory in RAM and inactive memory in an HDD to course contiguous addresses that hold an awarding and its data. Using virtual retentivity, a system tin load larger programs or multiple programs running at the same time, letting each operate as if information technology has infinite retentivity without having to add together more RAM.
Virtual memory is able to handle twice as many addresses every bit RAM. A program's instructions and data are initially stored at virtual addresses, and once the program is executed, those addresses are turned into actual memory addresses.
I downside to virtual retentivity is that information technology tin slow a computer considering data must exist mapped between the virtual and physical memory. With physical retentivity alone, programs piece of work straight from RAM.
RAM vs. wink memory
Flash memory and RAM are both comprised of solid-state chips. However, they play different roles in computer systems because of differences in the fashion they're made, their performance specifications and cost. Wink memory is used for storage retentivity. RAM is used as active retentivity that performs calculations on the data retrieved from storage.
I significant difference between RAM and flash memory is that data must be erased from NAND wink memory in unabridged blocks. This makes information technology slower than RAM, where data can be erased in individual bits.
All the same, NAND flash retention is less expensive than RAM, and it's as well nonvolatile. Dissimilar RAM, it can hold data even when the power is off. Considering of its slower speed, nonvolatility and lower cost, flash is often used for storage retention in SSDs.
RAM vs. ROM
Read-only retentiveness, or ROM, is figurer memory containing data that tin only exist read, not written to. ROM contains boot-upwards programming that is used each time a computer is turned on. Information technology generally can't be altered or reprogrammed.
The data in ROM is nonvolatile and isn't lost when the figurer power is turned off. As a consequence, read-but memory is used for permanent data storage. Random Access Retention, on the other paw, can just hold data temporarily. ROM is generally several megabytes of storage, while RAM is several gigabytes.
Trends and futurity directions
Resistive Random Admission Retentiveness (RRAM or ReRAM) is nonvolatile storage that tin alter the resistance of the solid dielectric material it'south composed of. ReRAM devices contain a memristor in which the resistance varies when different voltages are applied.
ReRAM creates oxygen vacancies, which are physical defects in a layer of oxide material. These vacancies represent ii values in a binary system, similar to a semiconductor'southward electrons and holes.
ReRAM has a higher switching speed compared to other nonvolatile storage technologies, such as NAND wink. It also holds the promise of loftier storage density and less power consumption than NAND wink. This makes ReRAM a practiced option for memory in sensors used for industrial, automotive and internet of things applications.
Vendors have struggled for years to develop ReRAM technology and get chips into product. A few vendors are currently shipping them.
3D XPoint technology, such as Intel'due south Optane, could eventually fill up the gap between dynamic RAM and NAND flash memory. 3D XPoint has a transistor-less, cross-point architecture in which selectors and memory cells are at the intersection of perpendicular wires. 3D XPoint isn't equally fast equally DRAM, only it is nonvolatile memory.

In terms of performance and price, 3D XPoint engineering is between fast, but costly DRAM and slower, less expensive NAND flash. Every bit the engineering science develops, it may mistiness the distinction between RAM and storage.
5G and the RAM market
In February 2019, the JEDEC Solid Country Technology Association published the JESD209-5, Low Power Double Data Rate 5 (LPDDR5). LPDDR5 will eventually operate at an I/O rate of 6400 MT/s, l percent higher than that of the first version of LPDDR4. This will significantly boost memory speed and efficiency for a variety of applications. This includes mobile computing devices such as smartphones, tablets and ultra-sparse notebooks.
LPDDR5 was published with a data rate of 6400 MT/s, compared to 3200 MT/due south for LPDDR4 at its publication in 2014.
In July 2019, Samsung Electronics began mass producing the industry's first 12-gigabit LPDDR5 mobile DRAM. According to Samsung, it has been optimized for enabling 5G and AI features in hereafter smartphones.
Cost of RAM
By the summertime of 2019, DRAM prices remained depressed from before levels -- but volatile, still. A number of variables contributed to the volatility, including:
- a supply glut
- market tensions between Republic of korea and Nippon (home to the world's two largest retention chip makers, Samsung and SK Hynix)
- the introduction of the next-generation mobile chip, the LPDDR5
- the increased adoption of 5G engineering
- an anticipated increment in need for consumer electronics in the Net of Things (IoT), such as automobiles and wearable devices, which use the chips
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchstorage/definition/RAM-random-access-memory
0 Response to "Randomly Lost Randomly Found Again in the Gaps of the Years"
Post a Comment